Can a smartwatch measure heart rate, blood oxygen levels, or sleep? Yes, smartwatches are filled with sensors that help your track various features, which we will explore in this article.
Smartwatches have gained popularity due to their high-tech capabilities and ease. They have certainly made a living more pleasant. But have you ever thought about how smartwatches work? If you have one, you can assess its value based on the many elements and metrics it monitors.
The smartwatches display the time and use cutting-edge technology to assess your heart rate, track different activities, measure blood oxygen levels, measure temperature, and much more. They are also your ultimate fitness partners and may be able to assist you with health-related issues. This article will tell you more about it and how smart watches work.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/38254022/moto360.0.0.jpeg)
1. Acceleration Sensor
The most prevalent form of a sensor in smartwatches is an acceleration sensor, which helps a smartwatch measure step counting. For example, a device’s location and movement may be determined by the acceleration sensor, which uses these parameters to determine if the device is in a vertical or horizontal position and whether or not it is moving.
Naturally, not all acceleration detectors are reliable. For example, the standard model has just two axes, which could be more accurate; however, the three-axis sensor can identify the device’s location in three-dimensional space and accomplish more precise recording.
It may be used inside and outdoors, is not impacted by weather, uses less electricity, and can retain sports data for many days. However, the number of steps for specific low-profile acceleration sensors might be created by shaking hands or swinging the arm in position, which impacts the accuracy of motion data.
2. ECG Sensor
The ECG sensor is a highly professional sensor directly connected to heart rate monitoring. This kind of sensor is similar to an ECG in that it helps the smartwatch measure the user’s heart rate by monitoring the electrical signal of myocardial contraction.
As a result of their high level of precision, these devices have a more complex circuit, which is susceptible to electromagnetic interference. And it’s at a fixed measuring position; otherwise, the findings would be skewed.
Another detecting technique used by the same ECG sensor is photoelectric detection. The photoelectric heart rate employs the photo volume approach, which involves shining a light on the wrist and measuring the light scattering of various blood flow rates. It’s less precise than a heart rate belt, but it’s easier to wear.
3. Satellite Sensor
Because all GPS-related gadgets must be linked through satellites, smartwatches with GPS functionality include satellite sensors.
They help a smartwatch measure the speed of movement and the distance covered per unit of time by receiving signals from alien satellites. The intensity of the satellite signal and the sampling rate influence the accuracy of the location signal.
Although GPS drains the battery too quickly, it may record the movement and synchronize it to the map, using the professional-grade star search capability.
If you need to utilize it to record outside running, the star search ability should be finished within 10s to ensure the journey’s efficiency and correctness. The search time may be reduced to the 30s for everyday navigation help.
4. UV Sensor
The ambient light sensor mimics the light sensitivity of human spectacles, can assess the time based on the brightness of the surrounding light, and significantly reduces the power consumption of the motion tracking equipment. This idea is borrowed from the UV sensor, which can be used on the watch to monitor the UV index in the light and perform the sunscreen reminder function.
5. Heart rate monitor
The professional heart rate monitoring feature is a bonus if you need to wear it as a fashionable watch. Users may utilize most of the functionalities to check the time, send text messages, record steps, etc.
If used as a sports watch, in addition to recording the course of the activity, the heart rate cannot be disregarded and must be monitored in real-time. As a result, smartwatches with ECG sensors and satellite sensors are preferable.
6. Gyroscope
Gyroscopes are sensors that detect the body’s rotational angular velocity and orientation. For example, a gyroscope on your wristwatch will inform you if you move your wrist to examine your smartwatch in a split second.
This sensor helps your smartwatch preserve battery life by shutting off the display after an extended period of inactivity.
7. Blood oxygen saturation (SpO2 Sensors)
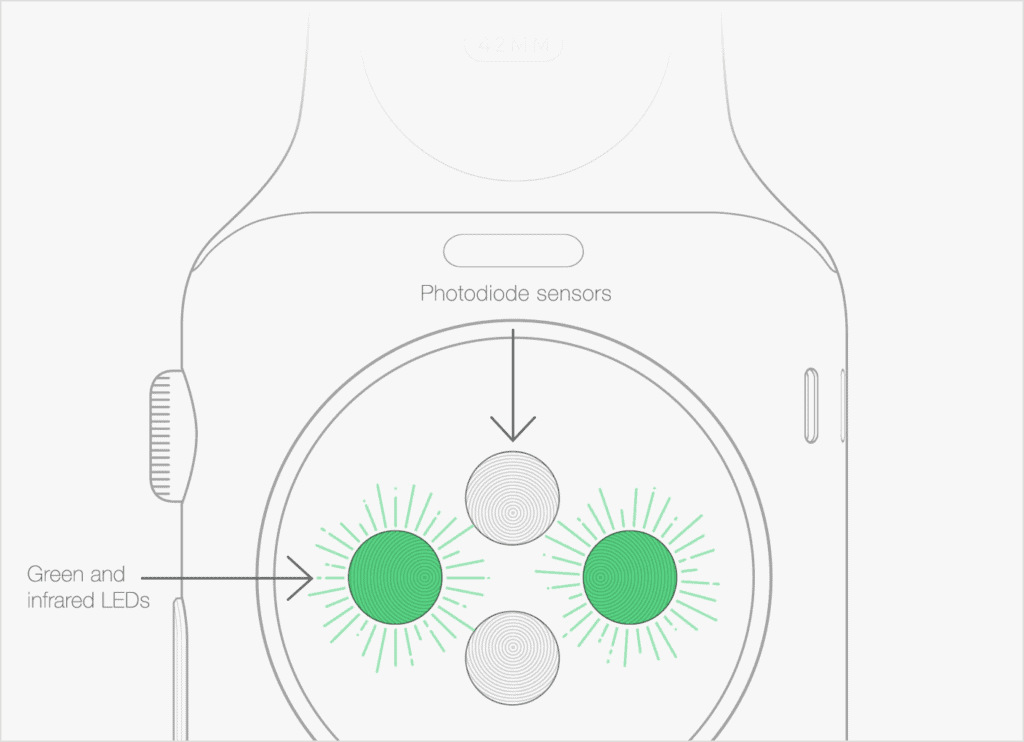
Pulse oximeters, often known as SpO2 sensors in fitness trackers, helo a smartwatch measure blood oxygen levels or oxygen saturation. Finger-based pulse oximeters are becoming more popular on smartwatches. However, medical-grade and wearable oximeters both need light to function.
A pulse oximeter typically has two LEDs with distinct light wavelengths, one red and one infrared. It is due to the differential in light absorption between blood with high oxygen levels and blood with low oxygen levels.
Oxygenated blood absorbs more infrared light than deoxygenated blood. As a result, pulse oximeters can now detect oxygen levels quickly and non-invasively, as well as monitor how effectively oxygen is transported to the extremities.
8. Electrodermal (EDA) Sensor:
Fitbit’s Fitbit Sense watch now has an electrodermal (EDA) sensor. Sensors may detect minor electrical changes in your skin’s perspiration level when you lay your hand over the device’s face.
Fitbit produces a stress management score between 1 and 100 based on your heart rate, sleep, and activity data, with a higher number indicating fewer physical indicators of stress and a lower number indicating more signs.
To assist you in managing stress, Fitbit may propose breathing exercises and other mindfulness methods. However, after a free trial time, you will be required to pay up for a paid membership service to delve further into the analytics.
A separate sensor on the Sense can detect changes in skin temperature. Apple and Samsung smartwatches do not currently support this functionality.
9. Sleep Trackers
Sleep monitoring is becoming more prevalent in the design of smartwatches. Sleep sensors help a smartwatch measure your sleep patterns. But how do they manage it? Smartwatches intend to monitor sleep accurately. They measure when you fall asleep, your sleep quality, how long you sleep, how long you spend in each sleep stage, your sleep surroundings, and other sleep-related health indicators.
When we sleep, we are virtually absolutely motionless compared to when we are awake. Body movement is, therefore, one helpful signal that smartwatches employ to inform us how much time we spend sleeping.
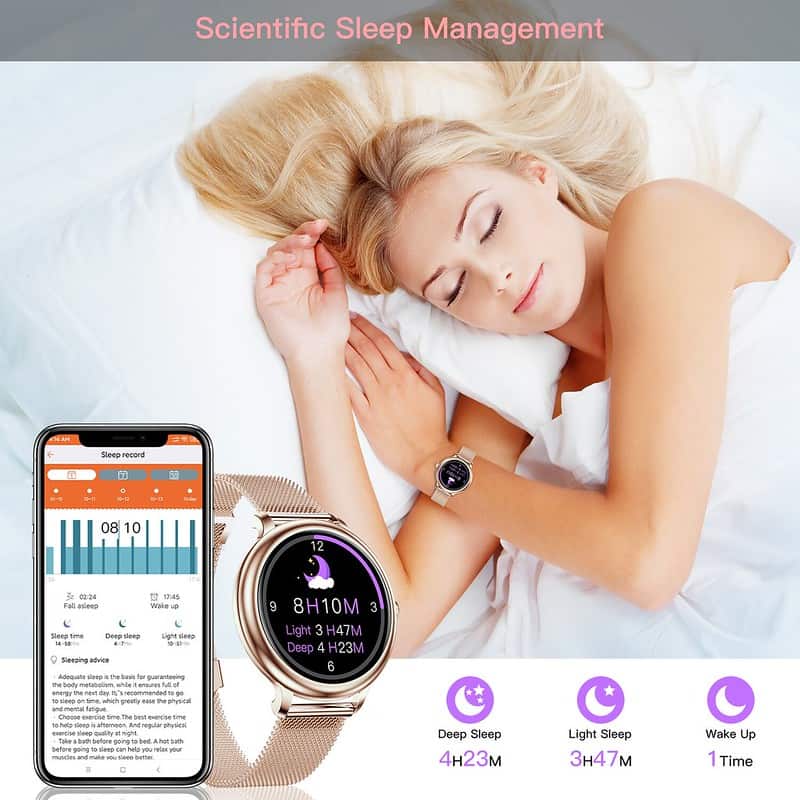
Depending on the smartwatch model, body movement is monitored via accelerometry or actigraphy. For example, wearable sleep trackers typically employ an actigraph sensor, while smartwatches use an accelerometer to record body movement and determine whether or not you are sleeping.
Aside from bodily movement, in a few cases, smartwatches assess various environmental and personal aspects to determine whether or not you are sleeping.
For example, they have a built-in microphone to record audio from your body or the environment. The presence or absence of noise may affect whether or not you are sleeping and offer information about the quality of your sleep. Furthermore, the microphone detects snoring by measuring your breathing.
10. Calories Sensors
Again, this is especially true for fitness trackers. They may help a smartwatch measure the estimated number of calories you have expended, the distance traveled, and the step count.
Our bodies burn calories when digesting, exercising, and performing critical bodily operations. Smartwatches compute the calories burned during physical exercise using the collected data of all other available sensors.
They keep track of many activities, such as walking to the shop on foot, running, etc. They employ information from various sensors, such as an accelerometer, and a separate algorithm, which varies across models, to estimate the number of calories burnt.
Based on these estimations, you may now determine what to drink, eat, and which exercise is ideal.
Conclusion
Many people need clarification as to what can a smartwatch measure. Constantly monitoring one’s blood pressure, heart rate, blood oxygen levels, and even stress levels may be bothersome for some. However, we can all agree that smartwatches make life so much easier.